Chapter 2: Evaluation Framework
The evaluation framework is the method used to determine the potential value of candidate technologies. A structured framework is required to ensure a uniform evaluation of technologies. This uniform structure will allow for comparisons of technologies within technology categories. However, even with a uniform evaluation framework, it is not appropriate to compare the performance of technologies across categories. The differences between technology categories are too great to allow an effective comparison of one technology to another across categories. Rather, this evaluation framework is designed to present the potential value of individual technologies with improved consideration of environmental concerns in transportation projects.
Therefore, the purpose of this effort is to, through technology application, improve consideration of environmental concerns in transportation decisions.
Two fundamental objectives have been generated to determine the potential value of these technologies: Technology Benefit and Technology Integration. The hierarchy below represents the association of the purpose with these two fundamental objectives.
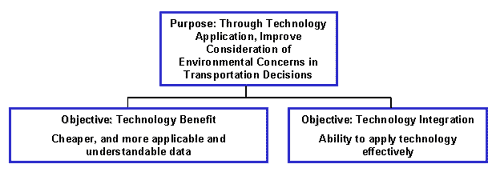
The potential value of a technology is both the benefit of value that an individual technology can provide in addition to the ability of an agency to effectively implement the technology. Technology benefit is the ability of the technology to move toward cheaper and more applicable and understandable data for project development. Technology integration is the likelihood and ability of an agency to implement the technology. These objectives lead to the purpose of technology application. The result is the combination of the technology benefit and the technology integration. Both must be considered in determining the value in meeting the purpose. If a technology can produce cheaper, more applicable, and/or more understandable data, yet is difficult to integrate, the value of the technology is questionable.
The basis for determining the potential value of technologies is through the application of evaluation criteria. Evaluation criteria were developed for both the Technology Benefit and Technology Integration objectives. The hierarchies below present the categories of criteria and the individual criteria.

The criteria categories are simply a means to organizing the criteria. The criteria are the measurable metrics that assess the performance of the technology. These categories and associated criteria were developed by the consultant team and improved by the Project Panel.
Technology Benefit is comprised of three categories of criteria:
- Cost and Schedule: How does the technology optimize cost and schedule of project development?
- Resource Management: How well does the technology assist in the management of natural and social resources?
- User-Friendliness of Data: How does the technology increase user-friendliness of the data to improve project acceptance with stakeholders and resource agencies and to ultimately improve proposing agency credibility?
Each of these categories are further refined into measurable criteria. The 14 measurable criteria identified in the above hierarchy will be used to evaluate Technology Benefit.
|
Technology Benefit |
|
|
Criteria |
Definition |
|
Cost and Schedule |
|
|
Reduction of work duplication |
To what degree does the technology assist with the reduction of work duplication? |
|
Early identification of fatal flaws/litigation potential |
To what degree does the technology provide early identification of fatal flaws and/or litigation potential of a program or project? |
|
Differential of cost from current technology |
What differential in cost does the new technology provide relative to the current technology? |
|
Reduction in uncertainty of cost |
To what degree does the technology provide insight in reducing the uncertainty of project costs? |
|
Time savings |
How well does the technology provide time savings in the environmental process? |
|
Resources Management |
|
|
Identification of resources |
How well does the technology perform with the identification of project/program resources? |
|
Improving understanding of trade-offs (avoidance versus mitigation) |
To what degree does the technology help improve the understanding of trade-offs between the avoidance of impacts and the mitigation of impacts? |
|
Improving understanding of potential impacts |
Rate the level to which the technology improves the understanding of potential impacts. |
|
Identification of mitigation strategies |
Rate how well the technology performs in regard to the identification of mitigation strategies. |
|
User-Friendliness of Data |
|
|
Improved availability of understandable information |
How well does the technology improve the availability of understandable information? |
|
Potential for engagement of stakeholders |
Rate the level to which the technology has the potential for engaging stakeholders in the environmental process. |
|
Ease of use of information |
To what degree is the information produced by the technology easy to use? |
|
Potential for multi-discipline interaction or collaboration |
Rate the technology for the potential of fostering multidisciplinary interaction or collaboration. |
|
Improved probability of permit approval |
To what degree does the technology improve the probability of receiving permit approvals? |
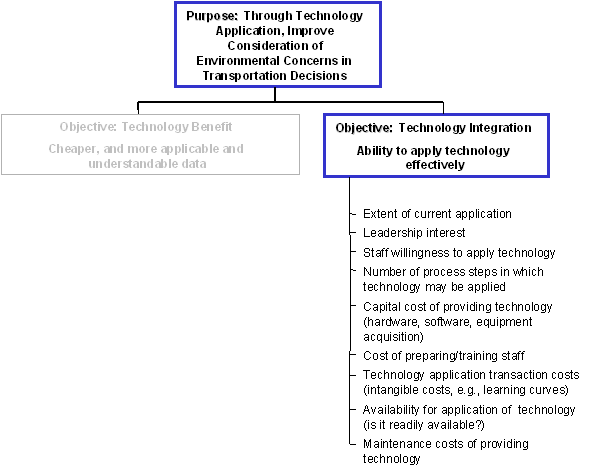
Technology Integration was also refined into measurable criteria. Nine criteria will be used to evaluate the possible integration of technology. No separate criteria categories are warranted.
|
Technology Integration |
|
|
Criteria |
Definition |
|
Extent of current application |
To what degree is the technology currently used in the transportation industry for application in the environmental process? |
|
Leadership interest |
What level of transportation leadership interest exists for implementing this technology? |
|
Staff willingness to apply technology |
How willing are transportation agency staff to apply this technology? |
|
Number of process steps in which technology may be applied |
How many transportation process steps may this technology be applied? 1-2 low, 3-5 moderate, more than 5 high |
|
Capital cost of providing technology (hardware, software, equipment acquisition) |
What are the capital costs for transportation agencies to provide the application of this technology? |
|
Cost of preparing/training staff |
What is the cost of preparing and training staff to utilize this technology? |
|
Technology application costs (intangible costs) |
What level of transaction costs are associated with the application of this technology? (Learning curve of staff, cost of transferring from one technology to another, etc.) |
|
Availability for application of technology (is it readily available?) |
Rate the level to which the technology is readily available for use. |
|
Maintenance costs of providing technology |
Rate the level of costs associated with maintaining the use of this technology: software licensing fees, continued training, etc. |
All proposed technologies will be evaluated against each criterion. To maintain
ease of application and consistency, a performance scale of 1 to 3 will be used
for all criteria:
1 = Low
2 = Moderate
3 = High
For example, when rating technologies against Reduction of Work Duplication (the first criterion under the Cost and Schedule category), a value of 1 would indicate a low reduction of duplication (the technology doesn’t really help), and a value of 3 would indicate a high reduction in duplication (the technology provides great value). In most of the criteria, the high number rating of 3 indicates the best condition. However, for four of the Technology Integration criteria, a rating of 3 indicates the worst condition. These four criteria include:
- Capital cost of providing technology (hardware, software, equipment acquisition)
- Cost of preparing/training staff
- Technology application costs (intangible costs)
- Maintenance costs of providing technology
All four involve the cost component of providing and using the technology. In the case of these four criteria, a high cost (3 rating) is the worst condition, and low cost (1 rating) is the best condition.
These criteria are applied to each individual technology. Results are provided in the rating sheets for each technology profile in Chapters 3 through 7.